Introduction
Have you ever wondered:
Why antibiotics are not panaceas?
Why antibiotics are not as effective?
Why are there numerous antibiotics for one purpose?
All these are due to antibiotics resistance!
To understand antibiotics resistance, we need to first learn more about bacteria!
Chemical Concept
What are bacteria?

Bacteria are prokaryotes, which consist of a single cell with a simple internal structure.
They are only a few micrometers in size.
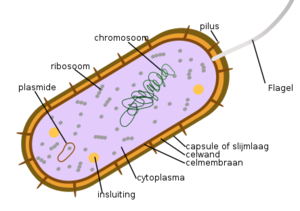

Bacteria generally appear in 3 different shapes- Spherical, Rod and Spiral.
These organisms can be found almost everywhere except for places that have been sterilized thoroughly. Some bacteria are found in extreme condition such as volcanoes, freezing polar regions and also deep underneath the ocean where pressure is high.
How Bacteria make us ill? / How bacteria cause illnesses?
When bacteria enters the body, they multiply and crowd body tissues to disrupt normal function kill the body cells and tissues by excreting chemicals that paralyzes the cell. They also can react in the body to produce toxins.

So how does the body get rid of bacteria?
Our immune system in our body will fight off foreign bacteria that weakens the body but if the infection is too serious, antibiotics is here help!

Antibiotics are medicines to treat infections/diseases caused by bacteria and parasites. Antibiotics can be taken orally, by injection or as creams, ointments or lotions to apply to skin.


The discovery of antibiotics by Sir Alexander Fleming have saved millions of lives since it was first publicly used.

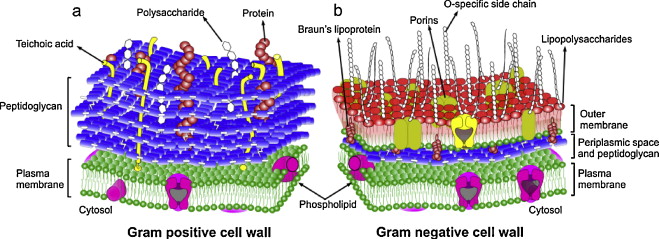
Gram Positive and Negative Bacteria
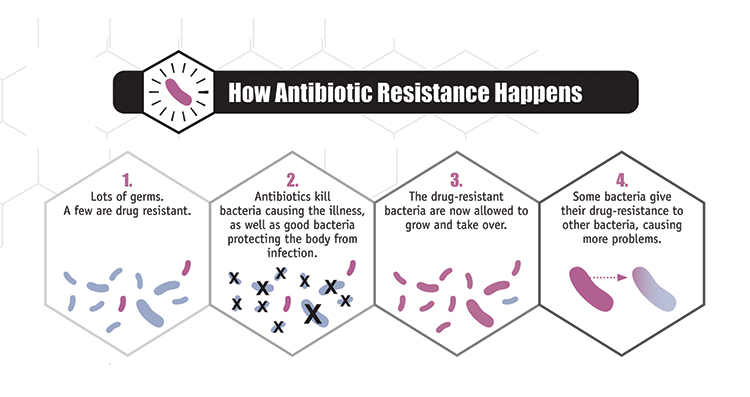
Antibiotic Resistance Process
Implication to Society



VIDEO: CHEMICAL CONCEPT
1st half of video
1.Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that are only a few micrometers in size (BACTERIA PICTURE)
2. Some bacteria are able to enter the body
- multiply and crowd body tissues to disrupt normal functions
- kill body cells and tissues by excreting chemicals
- react in the body to produce toxins.
3. Antibiotics are medicines to treat infections/diseases caused by bacteria
- target the cell wall of the bacteria and block the process by which bacteria combines molecules together. This causes the pressure in the cell to build up and eventually burst. (CELL WALL PICTURE)
- target the ribosomes in the cell of the bacteria. They prevent the ribosomes from producing proteins for the cell. Without proteins, the cell cannot to survive as proteins are the necessity to do work. (RIBOSOME PICTURE)

- target the DNA replication mechanism of the bacteria. (DNA REPLICATION PICTURE)
BUT
2nd half of video
4. Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics
- As a consequence of accumulated mutations in bacteria, some bacteria would already have antibiotic drug resistance (PICTURE 1/4)
- When bacteria is exposed to a antibiotic, those bacteria without resistance would be killed while those with resistance would continue to propagate (PICTURE 2/4)
- As such, it is expected that the new colonies of bacteria produced would all have antibiotic resistance (PICTURE 3/4)
- These new colonies of bacteria are then able to pass on their genes either through lateral transfer to other bacteria or vertical transfer to their offspring. (PICTURE 4/4)
5. Thus, development of antibiotic resistance becomes a problem as current antibiotics medicine loses its effectiveness as an increasing rate. We will look at the implication of this in the next video.
VIDEO: IMPLICATIONS TO SOCIETY
Misuse of antibiotics continues to promote development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.

- Main Causal factors
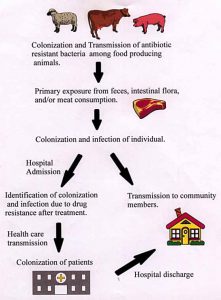
- Growing reliance on feeding antibiotics to livestock for:
- growth promotion (Genetically modified vs Farm)

- weight gain

- and to treat, control and prevent disease

- Path of bacteria from animals to humans
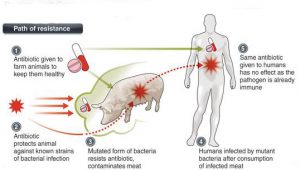
- Many cycles of food consumption from different sources : resistance sharing between bacteria leads to the formation of a super bacteria which is resistant to many drugs. Difficult to treat once it infects the patient as many antibiotics will not work.
- Path of bacteria from animals to humans
- Clinical overuse of antibiotics
- Effects
- Drive up drug and hospital cost:
- As antibiotic resistance spreads, more and more commonly used antibiotics must be retired. More funds must be funneled into development of new antibiotics, driving up the cost of antibiotics that are effective in treatment

- $20 billion in health care costs each year in the U.S. $35 billion loss in productivity

- As antibiotic resistance spreads, more and more commonly used antibiotics must be retired. More funds must be funneled into development of new antibiotics, driving up the cost of antibiotics that are effective in treatment
- Detrimental effects on human health:
- Ridding patients of infection requires longer treatment

- Greater disability and death due to absence of effective treatment



- e.g fatal diarrhea in children: children given antibiotics for routine upper respiratory infections are more susceptible to aggressive antibiotic-resistant strains of the bacteria clostridium difficile, commonly known as C-diff. Responsible for 250,000 infections in hospitalized patients and 14,000 deaths every year among children and adults

- Killing good bacteria with antibiotics


- May be contributing to rises in chronic health conditions such as obesity, asthma and cancer


- wipe out many good gut bacteria while leaving those immune to antibiotics to flourish.
- Drive up drug and hospital cost:
- Things professionals can do
- Prescribe antibiotics only for infections they believe to be caused by bacteria.

- Remind patients of the direction for proper use:
- Complete the full course of the drug.
- Do not skip doses.
- Do not save antibiotics.
- Do not take antibiotics prescribed for someone else.
- Talk with your health care professional when in doubt.


- Things we can do
- Use antibiotics only as prescribed by your doctor.
- Take the appropriate daily dosage and complete the entire course of treatment.
- Don’t pressure your doctor to give you an antibiotic prescription.

- (crop out picture, title and point #4)
- Ask your doctor for advice on how to treat symptoms.

- Practice good hygiene.
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after using the toilet, before eating, before preparing food and after handling fresh meat.

- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, and keep kitchen work surfaces clean.
- Make sure you or your children receive recommended vaccinations.

- Some recommended vaccines protect against bacterial infections, such as diphtheria and whooping cough (pertussis).
- Use antibiotics only as prescribed by your doctor.
