Topic: Neutralising the Threats of Acid Rain
What is acid rain?
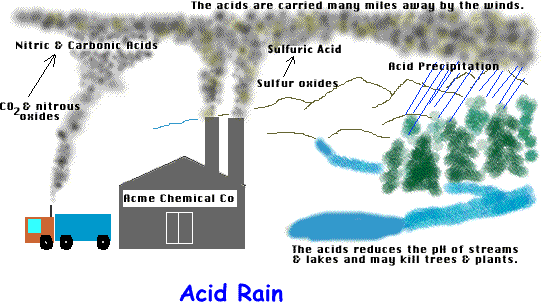
While rain is naturally acidic due to the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, acid rain is rain that has been made acidic by certain pollutants in the air. Acid rain is a type of acid deposition, which can appear in many forms. Wet deposition is rain, sleet, snow or fog that has become more acidic than normal. Dry deposition is another form of acid deposition, and this is when gases and dust particles become acidic. Both wet and dry deposition can be carried by the wind, sometimes for very long distances. Acid deposition in wet and dry forms falls on buildings, cars, and trees and can make lakes acidic. Acid deposition in dry form can be inhaled by people and cause health problems in some people.
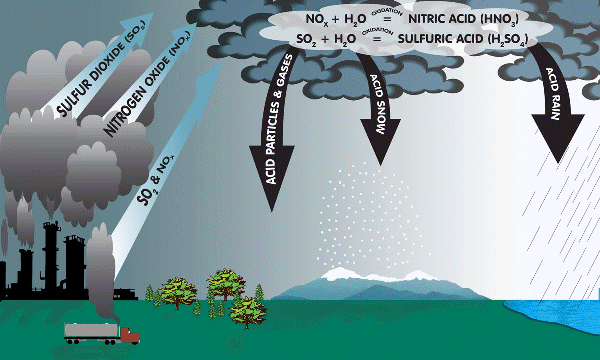
Where does it come from?
Acid rain is caused by chemical reaction of sulfur dioxides and nitrogen oxides. Power plants releases these harmful gases when they burn fossil fuels, such as coal, to produce electricity. The exhaust from cars, trucks, and buses are also a source of contribution.
Coal contains sulfur (S) and is burnt in power plants producing sulfur dioxide (SO2) that is poisonous.
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Sulfur dioxide can react with oxygen in the air to produce sulfur trioxide (SO3)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
Sulfur oxides (SOx) reacts with atmospheric water to produces acids.
SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
SO3 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq)
Atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen reacts together when high temperature is present forming nitrogen oxide (NO).
N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
Nitrogen oxides is highly reactive and reacts with hydroxyl radical, oxygen and volatile organic compounds (VOC) to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Nitrogen dioxide reacts with atmospheric water to form nitric acid.
NO2 (g) + H2O (l) + O2 (g) → HNO3 (aq)
Why is it harmful?
Acid rain is harmful as it contains acids which are hazardous compound in nature. List of some hazards of certain acids:
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4): 1) Corrosives 2) Acute Toxicity 3) Irritant 4) Health Hazard, carcinogen, reproductive toxicity, target organ toxicity
Nitric acid (HNO3): 1) Corrosives 2) Acute Toxicity 3) Irritant 4) Health Hazard, carcinogen, reproductive toxicity, target organ toxicity 5) Oxidisers





