The effects of acid rain is applicable to:
- People
- Aquatic ecosystem
- Trees & plants
- Buildings/sculptures
People:
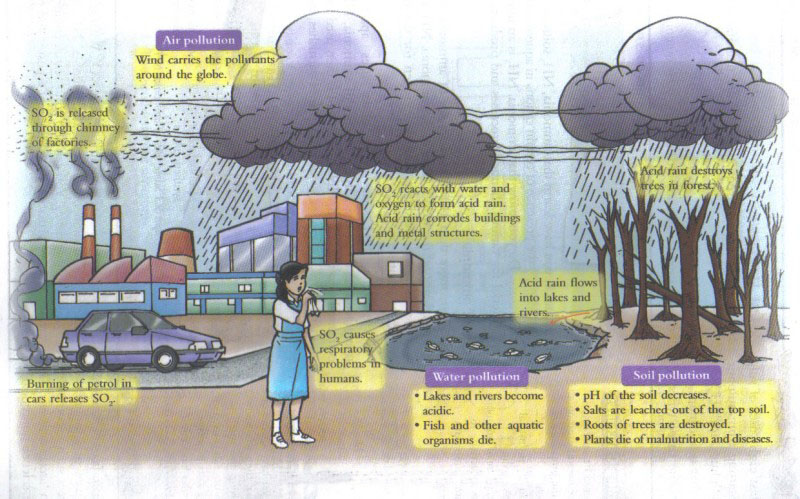
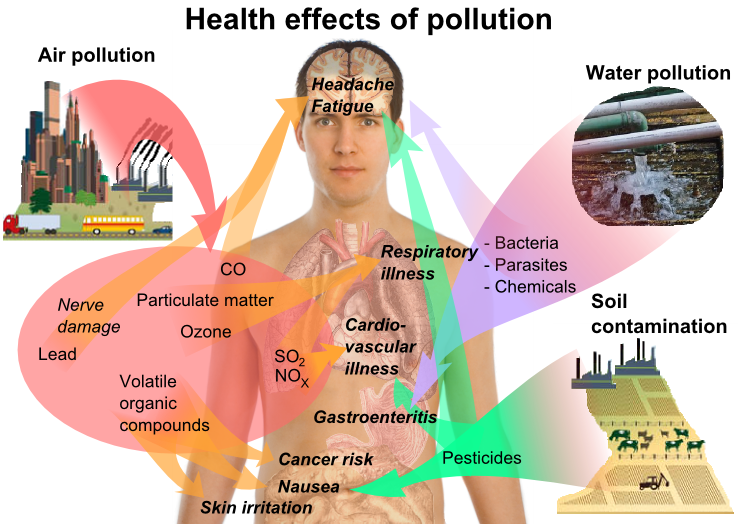
Acid rain can cause health problems in people. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are air pollution as they can create tiny particles which can cause respiratory diseases, or worsen them. Respiratory diseases such as asthma or chronic bronchitis make it hard for people to breathe, and when these tiny particles enter into our lungs, they can cause serious health problems.
Aquatic ecosystem:
Abundant wildlife exists in the ocean and lakes and pH is important in order to maintain a constant pH. pH is important for the homeostasis, growth rate and reproduction of aquatic animals and this is achieved by the presence of bicarbonate ions.
Acidic runoff releases aluminium from the soil, increasing toxic runoff into waterways, which is harmful to aquatic ecosystems. In the case of fish, when pH falls to 5, many fish eggs are unable to hatch, and the population may decline. At a pH lower than 5, adult fish may die. The survivability of these aquatic organisms differs at different pH level, depending on the critical pH level, for different species.


Trees & plants:
Humus and clay are negatively charged and will attract cations Ca2+, Mg2+. Cations of ions will be displaced and bound to the cell. Changes in pH of soil will increase the difficulty of trees to absorb water. It also decreases the immunity of trees and makes them susceptible to diseases, insect damage and temperature changes. When the trees die, there will be less shelter and food source that the tree act as for other land animals. This causes imbalance to the whole food chain of the ecosystem.
It is noted that trees which are of higher elevations experience more heavy impacts of acid rain. Soil does play a part in buffering acid rain, preventing pH levels increasing. However there are some areas where the soil’s “buffering capacity” is low and the harmful effects of acid rain will be observed to be much greater. A real life example will be the tree graveyard in Poland where the trees are completely stripped of vegetation due to acid rain.
Example: Czech Republic Forest


Building/sculptures:
Acids have a corrosive effect on limestone or marble buildings or sculptures. Sulfur dioxide increases the rate of corrosion on limestone, sandstone and marble. In a neutralisation reaction, sulfuric acid (H2SO4) will react with limestone (CaCO3) forming calcium sulfate (CaSO4) that is soluble in water. Hence, limestone dissolves and crumbles.
H2SO4 (aq) + CaCO3 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + H2CO3 (aq)
H2CO3 (aq) → CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
CaSO4 (s) +H2O (l) → Ca2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
Example:
Leshan Buddha (China)

Taj Mahal (India)

Colosseum (Rome)

Measures taken:
In the 1970s in the US, acid rain started to be noticed as a problem to the environment. In 1998, U.S. Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan testified before Congress on acid rain. He stated that the fishermen in the Adirondacks were experiencing a loss of fish in the remote lakes and asked for more action to be taken over the issue on acid rain.
The Clean Air Act which was enacted in 1990, attempted to target the issue through reducing the volume of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides produced
