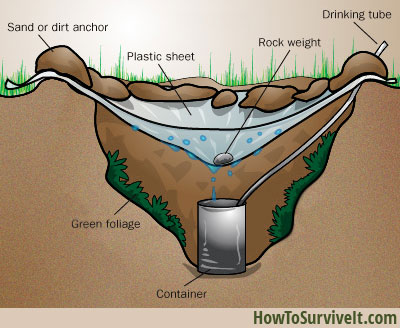
Q1) How can you purify your water when you are hiking? Name two or three possibilities. Compare these methods in terms of cost and effectiveness. Are they any of these methods similar to those used to purify municipal water supplies? Explain.
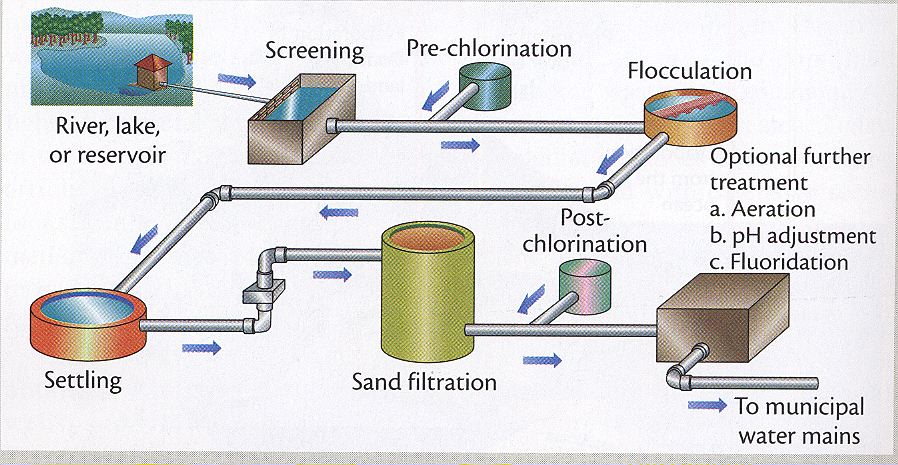
Municipal water purification methods include fluoridation, chlorination, coagulation, sedimentation and filtration to name a few. When hiking, the several methods available for us to obtain pure water follow the same approach as the municipal purification method.
For example, using sedimentation to obtain purified water is similar to the setting process in the municipal purification process. After sedimentation, filtration is required as well in order to separate the water from impurities.
Q2) Explain why desalination techniques, despite proven technological effectiveness, are not used more widely to produce potable drinking water.
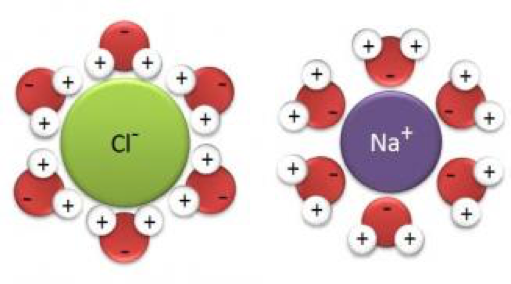
Desalination involves removes ions from seawater, namely NaCl. NaCl is an ionic compound that consist of both Na+ and Cl– ions. When dissolved in water, the ions will form ion dipole attractions with the water molecules as shown below.
These attractions are very strong and would require high amounts of energy to overcome. Energy consumption for the desalination process would hence be high making the process very costly in addition to the high cost of the technology used. Furthermore, the brine residue results in environmental concerns when being disposed.
Q3) Water quality in a chemical engineering building on campus was continuously monitored because testing indicated water from drinking fountains in the building had dissolved lead levels above those established by NEA.
a. What is the likely major source of the lead in the drinking water?
Major source of the lead is likely to come from corroded lead and iron pipes that distributes water to those drinking fountains. Due to the corrosion, lead seeps into the moving water and thus resulting in higher levels of dissolve lead in them.
b. Do the research activities carried out in this chemistry building account for the elevated lead levels found in the drinking water? Explain.
No, the research activities carried out in the chemical building may have nothing to do with the elevated lead levels found in the drinking water. There are several factors that may cause corrosion in the lead and iron pipelines, such as pH of the water, the amount of oxygen in the water, temperature of the water and the velocity of the water.
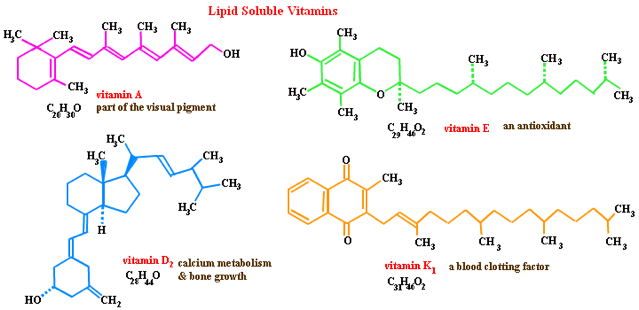
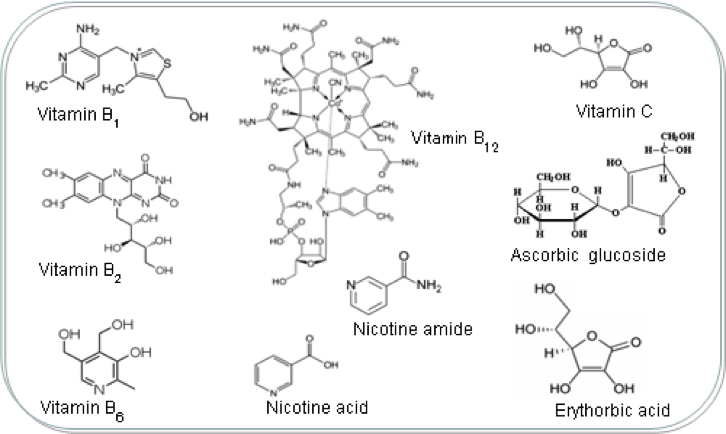
Q4) Some vitamins are water-soluble, whereas others are fat-soluble. Would you expect either or both to be polar compounds? Explain.
Both the water soluble and fat soluble vitamins would be polar compounds. The reason why water soluble vitamins are polar is because it has many polar parts such as -OH and C=O-O as seen in Figure 1, in which there are lone pairs in the O. Hence these areas are very electronegative, which results in the net dipole moment of the water soluble vitamins to be more negative than fat soluble vitamins. As such,more inter molecular hydrogen bonds can be formed between the hydrogen from one of the –OH with the lone pair from the oxygen from the another polar part such as –OH and C=O-O.
Figure. 1
Figure. 2
Fat soluble vitamins are also polar,just that it is less polar than water soluble vitamins.
As seen in Figure 2,the fat soluble vitamins usually have a long chain of carbon and hydrogen bonds,which is non polar.Hence the only polar areas in fat soluble vitamins would be those with –OH. Hence,the overall dipole moment of fat soluble vitamins are less negative as compared water soluble vitamins. Therefore, it is not very soluble in water since it does not form much inter molecular hydrogen bonds in water.


 Ozone layer gives an incorrect image of a blanket like layer in the stratospheric region of highest concentration.
Ozone layer gives an incorrect image of a blanket like layer in the stratospheric region of highest concentration.
