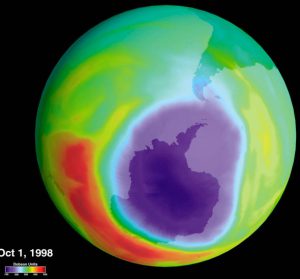
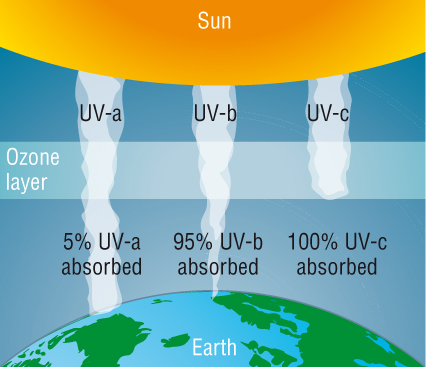
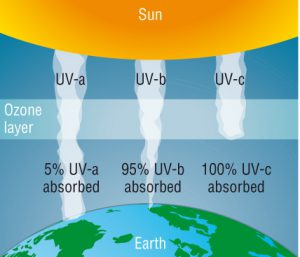
Question One:
Distillation. Impure water is evaporated, and pure water condenses on the plastic foil. The water then drips down into the cup collecting the pure water that is consumable.
Or we can just purchase water purifying equipment for hiking, like Ultraviolet Light Water Purifier.
Question Two:
Desalination using reverse osmosis techniques is costly to maintain the condition of the technology used, and it requires a high-energy consumption. Places usually use this where they do not have natural resources of water. (Eg. Singapore.) If they have natural resources, cities will use other cheaper ways to purify water, such as distillation.
Desalination will cause environmental problems as well, upsetting the ecosystem, and affect marine life since water is needed to be pumped from the sea, and pipes may vacuum and kill the marine-organisms.
Question Three:
- The main source is from the pipes that contain lead. The lead is dissolved into the water.
- In a chemistry lab, we practice the separation of aqueous and chlorinated waste. We do not dispose the lead into the sink. Hence, research activities cannot account for the elevated lead levels, unless someone do not practice safe disposal of chemical waste.
Question Four:
Whether the solute is soluble is dependent on the energy required to overcome the bonds between the solute-solute and solvent-solvent molecules, and the energy released due to the bonds formed between the solute and solvent molecules.
Water-soluble molecules would be polar compounds, due to similar bonding between water molecules being polar as well. The energy absorbed for bond breaking will be sufficiently compensated for the energy released from the bond formation between solute and solvent molecules.
Though a fat-soluble compound is often non-polar as fats are usually non-polar. This similarity in the polarity of the solute and solvent will result in sufficient energy for compensation provided by the bond formation, to support the bond breaking, making the reaction of solubility favourable.