So for the implications of air pollution on the personal level, there are several side effects from the various pollutants that can be present in the air.
The US EPA is required by the law to set air quality standards for six different pollutants. They are
- Ozone (O3)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Lead (Pb)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Particulate matter (US EPA, 2017)
OZONE
Ground level ozone is an indirect pollutant produce through the chemical reactions between oxides of nitrogen and volatile organic compound in the presence of sunlight. The major producers of such oxides of nitrogen include industrial and electrical facilities, motor vehicle exhaust and vapours from gasoline and chemical solvents (US EPA, 2017).
Ozone is believed to be responsible for coughing and pain when taking deep breaths, irritation in the lungs and throat, wheezing and difficulty breathing during strenuous or outdoor activities. The people most susceptible to the effects of ozone include the aged, young children, people with preexisting conditions such as asthma or other lung diseases as well as people that are required to engage in outdoor activities or work (CDC,2016).
So when Ozone concentrations are high, steps can be taken to limit the amount of ozone you are exposed to. You should spend more time indoors where ozone concentrations are lower, engage in less strenuous activities and plan outdoor activities when ozone concentrations are lower usually in the morning and evening (CDC,2016).
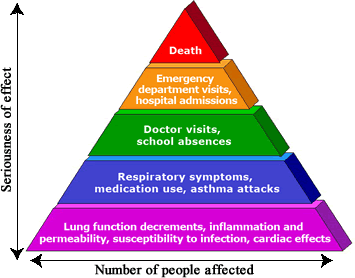
CARBON MONOXIDE
Carbon monoxide is the second pollutant that we are going to talk about. It is a colourless and odourless gas that is toxic when inhaled in high concentrations. It is produced mostly by any machinery that burns fossil fuels such as cars and other motor vehicles (US EPA, 2017).
Carbon monoxide poisoning happens when carbon monoxide builds up in the blood stream and replaces the oxygen that is carried by the haemoglobin, preventing oxygen from reaching your cells. This is a serious condition that can lead to tissue damage or even death in severe cases. People that are the most susceptible to such effects include unborn babies, as fetal cells take up carbon monoxide much more readily, Children, as young children have higher breath rates as compared to adults which makes them more susceptible, Older adults, as those that experience carbon monoxide poisoning at this age is more likely to develop brain damage, and people who have preexisting medical conditions such as heart diseases as they already have an impaired ability to transport oxygen to the body cells (Mayo clinic, 2017).

LEAD
The third pollutant that we going to talk about is lead. The main producers of lead emission and differ from area to area, but generally the most common source of lead are from ore and metal processing as well as mode of transports running on leaded fuel (US EPA, 2017).
Lead can have serious side effects on the health of the human body. At high concentrations, it is known that lead poisoning will compromise brain and central nervous system functions, leading to cma, convulsions and even death. Survivors of lead poisoning can still have mental and behavioural disorders.
At lower concentrations, lead was once thought to be safe, is now linked to a spectrum of injury in various body systems. Lead poisoning also result in anaemia, hypertension, renal impairment, immunotoxicity and toxicity to the reproductive organs. The neurological and behavioural effects of lead are believed to be irreversible. The young population is especially susceptible as they absorb 4–5 times as much ingested lead as adults from a given source. (WHO, 2017).

SULFUR DIOXIDE
The fourth pollutant that we are going to talk about is Sulfur dioxide. They are produced due to the burning of fuels with high sulfur content. Other sources include ore processing as well as natural sources such as volcanoes etc (US EPA, 2017).
Exposure to the gas can be dangerous for health. Exposure to concentrations exceeding 100 ppm is considered dangerous for life.
Symptoms can include burning in the nose and throat, breathing difficulties as well as serious airway obstructions. Long term exposure is known to affect lung functions. Those that are more susceptible to this chemicals include workers working in mines as well as those working in the field of fossil fuel extractions. This gas can be especially dangerous to people with preexisting medical conditions such as asthma and COPD (ATSDR, 2015).

NITROGEN DIOXIDE
The fifth pollutant that we are going to talk about is nitrogen dioxide. They are generally produced from the burning of fuels. They form from the emission from motor vehicles as well as other off road equipment.
Exposure to high concentration of nitrogen dioxide can irritate airways in the respiratory system. Short term exposure can increase the severity of respiratory diseases such as asthma and may result in coughing, wheezing and difficulty in breathing. Long term exposure can result in the development of asthma as will as a general increase in susceptibility to respiratory tract infections. People that are more susceptible to this effects include children, elderly as well as people with preexisting health conditions such as asthma. All oxides of nitrogen also have the ability to react with other chemicals present in the air to form ground level ozone and particulate matter which are both other common forms of air pollution (US EPA, 2017)

PARTICULATE MATTER
The last type of air pollution that we are going to talk about comes in the form of particulate matter. They can come in different sizes and can have varied composition but they are usually emitted directly from a source such as forest fires etc. They are commonly referred to as PM10 and PM2.5. PM1o is found to be responsible for increased chances of worsening of respiratory and cardiological diseases such as asthma, respiratory symptoms as well as heart conditions.
PM2.5 are known to be responsible for the production of reactive oxygen species in the body through various mechanism and ROS is believed to be the main cause of oxidative stress and damage to DNA. Damaged DNA, when not repaired, can lead to teratogenesis carcinogenesis, mutagenesis and other irreversible damages. It is als found that PM2.5 does not only damage DNA but also drive the replication of damaged DNA leading to cancer. People that are more susceptible to this form of pollution include people with preexisting lung or heart diseases, children and the elderly (US EPA, 2017).
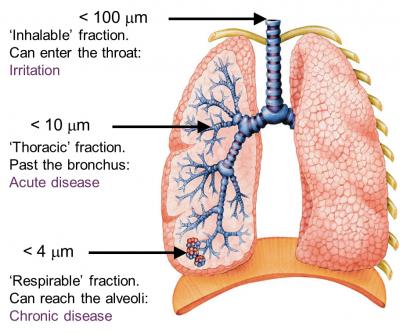
Source references:
http://philschimneysweep.co.uk/assets/images/phils/carbon-monoxide-poisoning-symptoms.jpg
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Complications – Mayo Clinic”. Mayo Clinic. N.p., 2017. Web. 1 Mar. 2017.
CDC – Air Quality – Ozone And Your Health”. Cdc.gov. N.p., 2017. Web. 1 Mar. 2017.
“Criteria Air Pollutants | US EPA”. Epa.gov. N.p., 2017. Web. 1 Mar. 2017.
“Lead Poisoning And Health”. World Health Organization. N.p., 2017. Web. 1 Mar. 2017.
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). 1998. Toxicological profile for Sulfur Dioxide. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service
Image references
http://lewistonauburnlead.org/wordpress/?page_id=8
https://www.epa.gov/ozone-pollution-and-your-patients-health/health-effects-ozone-general-population
https://www.slideshare.net/ravindra007/egr-presentation
https://www.cph.co.nz/your-health/air-quality/
https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/volcanic_ash/respiratory_effects.html